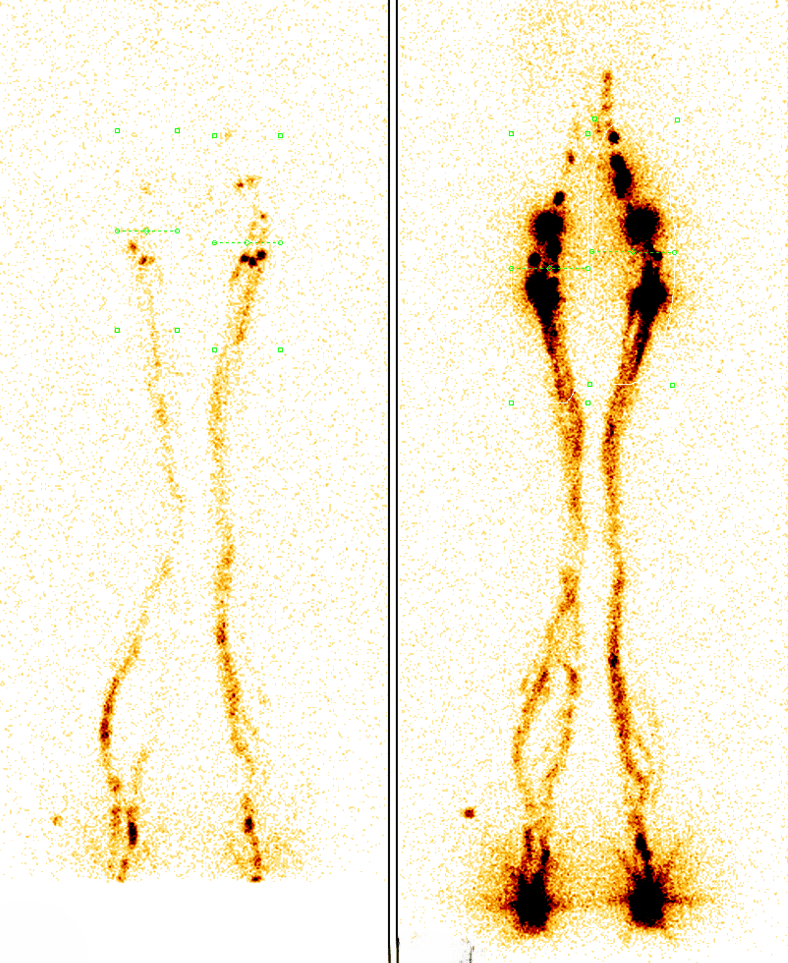Lymphoscintigraphy
A practical guide for referring physicians
Lymphoscintigraphy is a functional radionuclide examination that allows imaging of the flow and drainage of the lymphatic system, most commonly in the lower and upper limbs, but also in other parts of the body. After subcutaneous administration of a small dose of a colloidal radiopharmaceutical labelled with 99mTc (most commonly nanocolloid or antimony sulphide), the dynamic transport of particles through the lymphatic pathways and their accumulation in regional nodes is monitored.
The examination provides valuable information about the patency of the lymphatic pathways, the presence of blockages or collaterals, and differences between the right and left sides. It is non-invasive, well tolerated, and has a very low radiation exposure.
- Chronic swelling of the limbs – differential diagnosis of lymphoedema vs. venous oedema
- Primary lymphoedema – congenital abnormalities of the lymphatic pathways
- Secondary lymphoedema – after surgery, radiotherapy or injury
- Evaluation of treatment effectiveness – physiotherapy, compression therapy, surgical procedures
- Planning surgical procedures – microsurgical reconstruction of lymphatic vessels
Interpretation
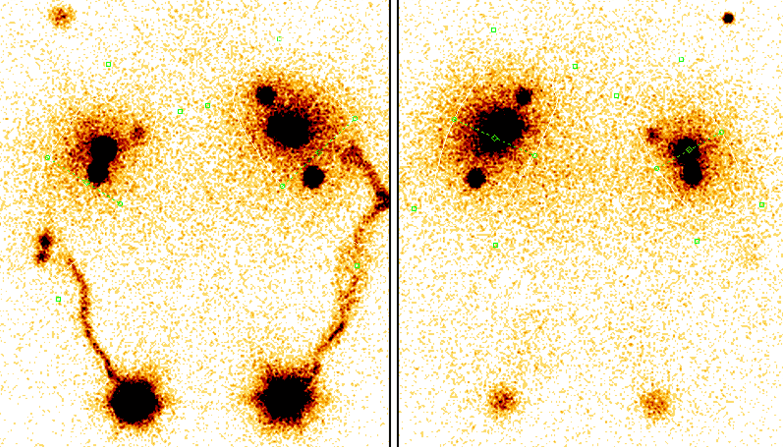
- Normal findings: rapid symmetrical transport of radiopharmaceuticals to regional nodes
- Pathological findings: delayed transport, absence of lymph node visualisation, collateral flow, dermal backflow
- The advantage is its functional nature – it provides information about patency and flow dynamics, not just anatomy
Practical information for the referring physician
- Patient preparation: no preparation
- Examination duration: 1–3 hours depending on the course of radiopharmaceutical transport
- Radiation exposure: very low (<1 mSv)
- Contraindications: practically none, relative in pregnant women
Summary for practice:
Lymphoscintigraphy is:
- the basic method for functional evaluation of the lymphatic system,
- indispensable in the differential diagnosis of oedema,
- suitable for planning and monitoring the treatment of lymphoedema.
Thanks to its simplicity, safety and low radiation dose, it is widely used across disciplines – from internal medicine and angiology to oncology and surgery.