Dynamic renal scintigraphy with pharmacological intervention – detection of renovascular hypertension (captopril test)
A practical guide for referring physicians
Principle and method
Renovascular hypertension (RVH) is a form of secondary hypertension caused by haemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis, which leads to activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Its early detection is of fundamental importance, as it is a potentially treatable cause of arterial hypertension.
Dynamic renal scintigraphy using 99mTc-MAG3 is used for diagnosis. The examination is supplemented by pharmacological intervention with an ACE inhibitor (enalapril i.v.).
Mechanism:
- In haemodynamically significant stenosis, glomerular filtration depends on increased efferent arteriolar tone induced by angiotensin II.
- After administration of an ACE inhibitor, this mechanism is eliminated → there is a decrease in the filtration function of the affected kidney.
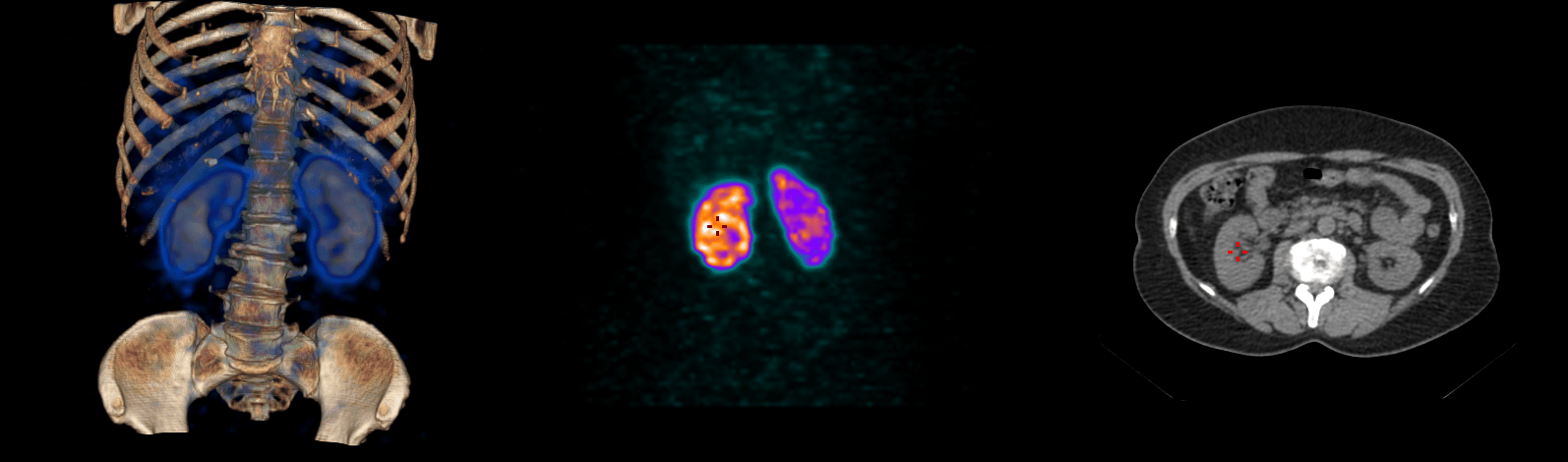
- The result is reflected in the scintigraphic curve as delayed excretion of the radiopharmaceutical.
Main clinical indications
- Suspected renovascular hypertension in patients with:
- severe, malignant or resistant arterial hypertension,
- sudden worsening of previously compensated hypertension,
- hypertension associated with renal insufficiency.
- Suspected renal artery stenosis based on ultrasound, CT angiography or MR angiography.
- Distinguishing functionally significant stenosis from incidental angiographic findings.
- Assessment of renal functional reserve prior to revascularisation procedures (angioplasty, stenting, bypass).
Interpretation
Positive finding
- Normal course before administration of ACE inhibitor, but after administration:
- delayed excretory phase,
- prolonged time to peak curve (Tmax),
- reduced parenchymal activity compared to the contralateral kidney.
Negative finding
- Stable curves without significant change after administration of ACE inhibitor.
Practical information for the referring physician
- Patient preparation:
- discontinuation of ACE inhibitors and ARBs at least 48 hours prior to the examination (if clinically possible),
- adequate hydration, empty bladder,
- Examination procedure:
- Performed in two steps:
- basal dynamic nephrography,
- dynamic nephrography after administration of enalapril
- Performed in two steps:
- Duration of the examination: approx. 60–90 minutes.
- Radiation exposure: low, usually less than 1 mSv.
- Contraindications: pregnancy; relative contraindications – allergy to ACE inhibitors, severe hypotension.
Summary for practice
Renal scintigraphy with captopril test is:
- a sensitive functional method for detecting renovascular hypertension,
- capable of distinguishing whether angiographic stenosis is haemodynamically significant,
- useful in selecting patients for revascularisation procedures,
- safe, simple and less costly than morphological imaging methods.
Correct indication and correlation with clinical and angiographic findings significantly increase its value in the diagnosis and management of patients with severe arterial hypertension.